What is WordPress

WordPress is a popular and widely used content management system (CMS) that allows users to create and manage websites and blogs. It provides a user-friendly interface for building and customizing websites without requiring extensive technical knowledge. WP is open-source software, which means it is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute.
WordPress offers a wide range of features and functionalities, including customizable themes, plugins for extending functionality, built-in SEO tools, media management capabilities, user management, and more. It powers millions of websites across the internet, ranging from personal blogs to large corporate websites and e-commerce stores.
One of the key advantages of WP is its flexibility and scalability. Users can start with a simple blog and expand it into a full-fledged website or online store as their needs grow. Additionally, the large community of developers and users contributes to its ecosystem by creating themes, plugins, and providing support and resources for users.
Overall, WP has become a go-to choice for individuals and businesses looking to create and manage their online presence efficiently and effectively.
Table of Contents
What is Blog?
A blog is a regularly updated website or web page, typically run by an individual or a small group, that is written in an informal or conversational style. Blogs often focus on a particular subject or niche, such as food, fashion, technology, or personal experiences. They can serve various purposes, including sharing knowledge, expressing opinions, documenting experiences, promoting products or services, or building a community around a common interest. Blogs typically feature posts arranged in reverse chronological order, with the most recent content appearing first. They often allow readers to interact through comments, creating a sense of engagement and community.
What are the Advantages of WordPress

- User-Friendly Interface: WordPress provides a intuitive dashboard and editor that makes it easy for users of all skill levels to create and manage content.
- Customization Options: With thousands of free and premium themes and plugins available, you can customize the look and functionality of your blog to suit your needs and preferences.
- SEO-Friendly: WP is built with search engine optimization (SEO) in mind, making it easier for your blog posts to rank higher in search engine results and attract more organic traffic.
- Scalability: Whether you’re starting with a simple blog or planning to expand into a full-fledged website or e-commerce store, WP can scale to accommodate your needs.
- Community Support: WP has a large and active community of developers, designers, and users who contribute themes, plugins, tutorials, and support forums to help you get the most out of your blog.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Most WP themes are mobile-responsive, meaning your blog will look and function well on a variety of devices, including smartphones and tablets.
- Built-in Blogging Features: WP was originally designed as a blogging platform, so it includes all the essential features you need to create and manage a blog, such as categories, tags, comments, RSS feeds, and more.
- Cost-Effectiveness: WP itself is free to use, and many of the themes and plugins available are also free or offer affordable pricing options, making it a cost-effective choice for bloggers on a budget.
How to Create a Blog at WordPress
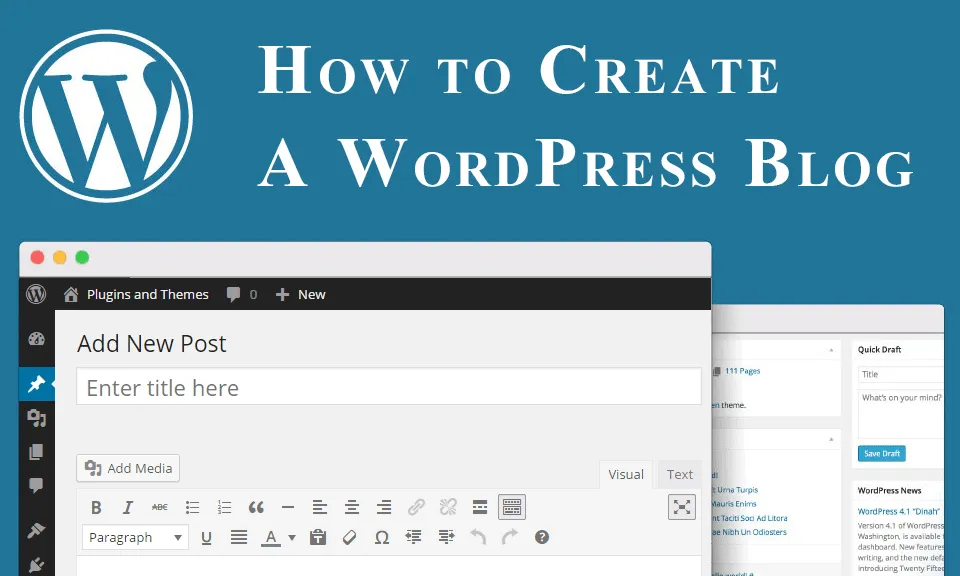
Creating a blog in WordPress is relatively straightforward. Here’s a basic guide to get you started:
- Sign up for Web Hosting: You’ll need a web hosting provider to host your WordPress website.
- Install WordPress: Most web hosting providers offer a one-click WordPress installation feature. Log in to your hosting account’s control panel (cPanel) and look for the “WordPress” or “Softaculous” installer. Follow the on-screen instructions to install WordPress on your domain.
- Choose a Theme: Once WordPress is installed, log in to your WordPress dashboard (usually located at yourdomain.com/wp-admin) using the credentials you set during installation. Go to the “Appearance” > “Themes” section and choose a theme for your blog. WordPress offers both free and premium themes, or you can upload a custom theme if you have one.
- Customize Your Blog: After selecting a theme, you can customize your blog’s appearance and layout using the WP Customizer. You can change colors, fonts, background images, and more to match your preferences and branding.
- Create Blog Posts: To start writing blog posts, go to the “Posts” > “Add New” section in your WPs dashboard. Enter a title for your post and add your content using the built-in editor. You can format text, add images, embed videos, and more.
- Add Categories and Tags: Organize your blog posts by assigning them to categories and adding relevant tags. Categories help visitors navigate your blog, while tags provide more specific topics for individual posts.
- Set up Navigation Menus: Create navigation menus to help users find their way around your blog. Go to the “Appearance” > “Menus” section in your WordPress dashboard to create and customize menus that include links to your blog pages, categories, and other important sections.
- Install Essential Plugins: WordPress plugins extend the functionality of your blog. Some essential plugins for a blog include Yoast SEO (for search engine optimization), Akismet (for spam protection), and Jetpack (for security and performance enhancements). You can install plugins by going to the “Plugins” > “Add New” section in your dashboard.
- Publish Your Blog: Once you’ve customized your blog and created some blog posts, it’s time to publish it for the world to see. You can do this by going to the “Settings” > “General” section in your dashboard and setting the visibility of your site to “Public.”
- Promote Your Blog: Share your blog posts on social media, engage with your audience, and consider implementing strategies to grow your blog’s traffic, such as search engine optimization (SEO) and email marketing.