What is Domain name

A domain name is a unique and human-readable web address that serves as the online identity of a website. It’s composed of two main parts: the actual name (e.g., “example”) and the domain extension (e.g., “.com”, “.org”, “.net”). Domain names are used to locate and identify specific websites on the internet, making it easier for users to access them. They play a crucial role in branding, marketing, and establishing credibility online. Domain names are registered through domain registrars and must be renewed periodically to maintain ownership.
Table of Contents
What is Domain name Renewal

Domain name renewal is the process of extending the registration period for a specific domain name. When you register a domain name, you typically do so for a set period, such as one year or multiple years. Before the registration period expires, you have the option to renew the domain name to maintain ownership and control over it.
Renewing a domain name involves paying a renewal fee to the domain registrar, the company through which the domain was initially registered. The renewal process typically occurs through the registrar’s website or online portal, where you log in to your account, select the domain name you wish to renew, and complete the renewal transaction.
It’s essential to renew your domain name before it expires to prevent it from being released back into the pool of available domain names, where it could be registered by someone else. If a domain name expires and is not renewed within a certain grace period, it may enter a redemption period, during which additional fees may apply to renew it. Failure to renew a domain name can result in loss of access to associated website and email services, as well as potential damage to your online brand identity and reputation.
What’s the Lifecycle of a Domain Name?
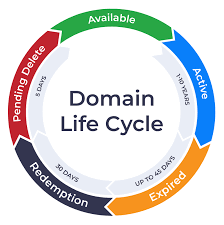
The lifecycle of a domain name typically involves several stages:
- Registration: The domain name is registered through a domain registrar for a specific period, usually one year or longer.
- Active: During this stage, the domain name is active, and it resolves to the associated website or online services.
- Renewal: As the expiration date approaches, the domain owner has the option to renew the domain name for another period, ensuring its continued use.
- Grace Period: After the expiration date, some registrars offer a grace period during which the domain owner can still renew the domain without penalty. However, the website or services associated with the domain may be suspended during this time.
- Redemption Period: If the domain is not renewed during the grace period, it enters a redemption period. During this phase, the domain can still be renewed, but additional fees are typically required.
- Pending Delete: If the domain is not redeemed during the redemption period, it enters the pending delete phase, during which it is removed from the domain registry.
- Release: After the pending delete phase, the domain is released back into the pool of available domain names, where it can be registered by anyone on a first-come, first-served basis.
The lifecycle of a domain name is essential for managing and maintaining your online presence effectively. It’s crucial to keep track of domain name renewal dates and take action promptly to avoid disruptions to your website and online services.
What Should You Need To Know About Domain Name Renewal

When it comes to domain name renewal, there are several key things to know:
- Expiration Date Awareness: Be aware of the expiration date of your domain name registration. Keep track of it to ensure timely domain name renewal.
- Renewal Options: Decide on the renewal period that suits your needs and budget, whether it’s annually, biennially, or longer.
- Auto-Renewal: Consider enabling auto-renewal to avoid accidental expiration. This feature automatically renews your domain name each year, ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Verify Contact Information: Ensure your contact information with the registrar is up to date to receive renewal reminders and notifications.
- Budget Planning: Renewal fees can vary between registrars and domain extensions. Budget accordingly to avoid surprises.
- Consolidate Registrations: If you have multiple domain names, consider consolidating them under one registrar for easier management and potential cost savings.
- Review Pricing: Check if your registrar has increased renewal fees since your initial registration.
- Transfer Consideration: Research the process and potential costs associated with transferring your domain to a new registrar if you’re dissatisfied with your current one.
- Ownership Confirmation: Ensure your domain is registered in your name or your organization’s name to prevent complications in the future.
- Renewal Grace Period: Understand the grace period after your domain name renewal that expires and any associated fees or redemption processes.
- Protect Your Brand: Consider registering variations of your domain name renewal and relevant extensions to protect your brand from competitors or malicious entities.
- Legal Obligations: Familiarize yourself with any legal obligations related to domain ownership, such as WHOIS information compliance.